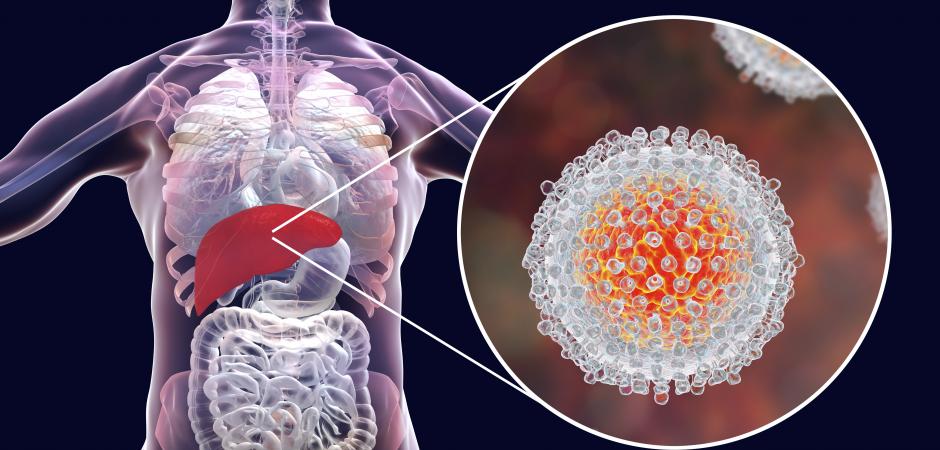
Hepatitis C is a virus that affects the cells in the liver. It is a constant irritant to these cells, which can cause the liver tissue to develop scar tissue. This can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), baby boomers (those born between 1945 and 1965) are five times more likely to have hepatitis C than other adults. Astonishingly, most people who have the disease don’t even know they are infected. That’s because people can live with hepatitis C for years and not show any symptoms or have feelings of sickness.
The good news is that there are hepatitis C treatments available that have a cure rate of over 95%. Your health team at UT Health North Campus Tyler is taking a proactive step in testing patients for this liver disease. It’s a simple blood test that can detect the infection. If the test is positive, the right measures can be taken, including treatment.
Who should I be tested for hepatitis C?*
- Anyone born between 1945 – 1965.
- Anyone who received blood or organs before 1992.
- Anyone with abnormal liver tests or liver disease.
- Anyone with medical conditions that impact the liver, like liver disease, HIV or AIDS.
- Health and safety workers who have been exposed to blood on the job through a needle stick or injury with a sharp object.
- Anyone on hemodialysis.
- Anyone born to a mother with hepatitis C.
- Anyone who has used a needle to inject drugs.
- One-time testing for all adults (18 years and older).
- All pregnant women during each pregnancy.
Why get tested?*
- Hepatitis C affects millions of Americans, but most don’t know it.
- It’s estimated that 8 in 10 people with hepatitis C develop a lifelong infection.
- There are often no symptoms associated with the disease.
- Chronic liver disease and liver cancer caused by Hepatits C are a common reason for liver transplants in the U.S.
- Hepatitis C can be treated and cured with medication in the majority of patients with this disease.
What are my next steps?
- Make an appointment with your primary care physician at one of our family medicine clinics.
- Your provider will order a blood test to determine if you have hepatitis C.
- If the blood test is positive, call 903-877-7162 to make an appointment with one of our gastroenterologist who have the expertise to treat hepatitis C.
*Recommendations from the CDC



